Networks are rapidly becoming larger and more complex, with numerous technologies playing into their growth and expansion. Network mapping has become increasingly important for administrators and managers tasked with handling these growing networks. Though the process of local area network (LAN) mapping can be performed manually, this manual work is risky, as there’s a higher chance something will be missed when it involves highly complex networks.
- Best Network Mapper Free
- Best Network Mapper Software
- Best Network Marketing Companies
- Best Network Mapper Free


SolarWinds Network Topology Mapper (Free Trial) SolarWinds has acquired a solid reputation in the field of network administration tools. In the past 20 years, the company has made quite a few excellent network administration tools. The company is also famous for its free tools. SolarWinds Network Topology Mapper is a highly sophisticated network topology tool offering a wide range of functionalities. This network mapping solution can automatically discover and map your complete network topology, displaying the structure and how each component connects in easy-to-interpret, dynamic diagrams.
With the significant amount of network topology mapping software available on the market these days, I decided to review the tools network pros need to check out to help reduce their workloads and improve accuracy. I go over why SolarWinds® Network Topology Mapper (NTM) is a top choice for those looking for high-quality mapping software. Spoiler alert: this tool uses the best network mapping techniques to automatically discover your network topology, and it creates several types of informative visualizations, allowing you to easily see and navigate your network. And if you need a more comprehensive monitoring solution, I explain why SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor (NPM) is a good all-in-one option for those looking for a tool with other essential performance measuring tools in addition to a network topology mapper.
But First: What Is Network Mapping?
Network topology mapping is the process of visually and logically mapping the network to understand the connections between the server and different nodes. Network performance software and tools usually include some network mapping features to help optimize the network.
Network maps are useful resources when admins conduct performance monitoring processes to check each part of the network. Maps can help show where performance bottlenecks exist and where there are opportunities to improve, improving service quality for end-users. Network performance monitoring outputs admins can visualize in network maps include metrics like the latency between the server and clients, bandwidth, throughput, and errors or failures.
Why You Should Use a Network Topology Mapper
Network topology mapping gives you a high degree of visibility into your network and the relationships between your network devices. This visibility can be extremely useful for everything from troubleshooting problems to maintaining network security. Even if you use the best network mapping techniques, manual mapping is a time-consuming process often resulting in incomplete topology diagrams if you don’t keep up with each new device added to or removed from your network.
You should use a network topology mapper to make sure your network topology diagrams are always up-to-date. A robust network topology mapper offers network admins the tools they need to map networks at any scale, from the smallest business to the biggest enterprise. It also lets you map a specific packet pathway for help with traffic bottlenecks and service provider status. With a network topology mapper, admins can see a device’s status as well as its logical connections at the touch of a button. In short, if you’re interested in having a topology map capable of giving you the insights you need to improve your network performance, you need to use a network topology mapper.
Top Network Mapping Techniques
There are a few ways to think about network mapping techniques. The first is to consider physical vs. logical topology mapping. Physical mapping is all about the concrete network, from cables to terminations. Logical network mapping is more common, and it focuses on data behavior within the networked environment rather than the physical layer. A logical network map is appropriate for a greater range of use cases, as it provides an accurate sense of how the network’s data actually works, with insight into features like routers, subnets, and so on. However, a physical map can be useful for network engineers.
Another way to think about network mapping techniques is to consider manual, semi-automated, and fully automated techniques for creating maps. Manual maps take time to create and aren’t useful for highly dynamic networks. But a manually created Visio map can be useful if you want to create a highly complex, nested map to fit unique specifications.
For most, semi-automated or automated network topology mapping is more useful and feasible. A semi-automated map might be able to automatically discover new devices on the network, but you’ll still need to take steps to position devices and set connections correctly. Automated network topology mapping is responsive to your network environment as it changes, adjusting devices, their connections, and the performance of those connections on an ongoing basis to display an updated and complete logical map.
To optimize your network topology mapping efforts, you should invest in a tool capable of automating the mapping process, creating an initial network map when it’s first installed, and regularly scanning your network to ensure the map always reflects your current network and device relationships. The best network topology mappers will also be configurable and customizable, allowing you to adjust the frequency of network scans and easily create visual representations of different aspects of your network.
Best Network Mapping Tools
I believe using network mapping software is a vital step in managing your network efficiently and professionally in any business setting. There are several tools you can use, including some free network topology mapper tools, but I recommend a couple of products due to their extensive feature lists and easy-to-use nature.
Network Topology Mapper
SolarWinds Network Topology Mapper is a dedicated network mapping tool. It automatically discovers and maps out your network topology and shows you the structure of your network in easy-to-view diagrams.
From a single network scan, NTM can build multiple maps, allowing you to compare and choose the map best suited to your needs. It also integrates well with other software, allowing you to export to Microsoft Office Visio as well as PDF and PNG formats. You can try NTM free for 14 days.
Network Performance Monitor
For a more comprehensive network topology mapper with additional features, I recommend SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor. NPM includes packet-level network topology insights (including cloud and VMware environments) and also offers great Wi-Fi heat mapping tools.
With the NetPath™ function, you can gain insight not just into your own network but into data pathways all the way to destination services. You can see hop-by-hop packet paths and instantly know where issues are occurring. You also get features such as the PerfStack™ dashboard, which allows you to compare the performance of different metrics side by side.
NPM includes troubleshooting features and alerts and is designed to be an easily scalable and reliable centralized network management tool. This is my pick if you want a truly comprehensive tool for provisioning and maintaining your network topology. You can get more information about the features of this network mapping tool here.
PRTG Network Monitor
PRTG Network Monitor is another comprehensive network topology mapping software offering network monitoring for the entire network, including network traffic, application performance, cloud services, and database capacity as well as network uptime, security, and hardware longevity. You can use it for network topology mapping, as it allows you to create maps using the PRTG map designer. This is a manual process, but once you’ve created the maps, you can use them to view network information in real time for your devices, connections, and status updates. This software is on the pricier end for what it offers.
Intermapper
Another great option for network mapping software is the Intermapper tool by HelpSystems. The Intermapper tool has both network mapping and network performance monitoring features, and it has cross-vendor support for Cisco, Apple, Dell, and more. With an intuitive and clear display, it provides a fully customizable network map, allowing you to see real-time network health with color-coded animations. You can choose either device-based pricing or a flat fee for unlimited devices.
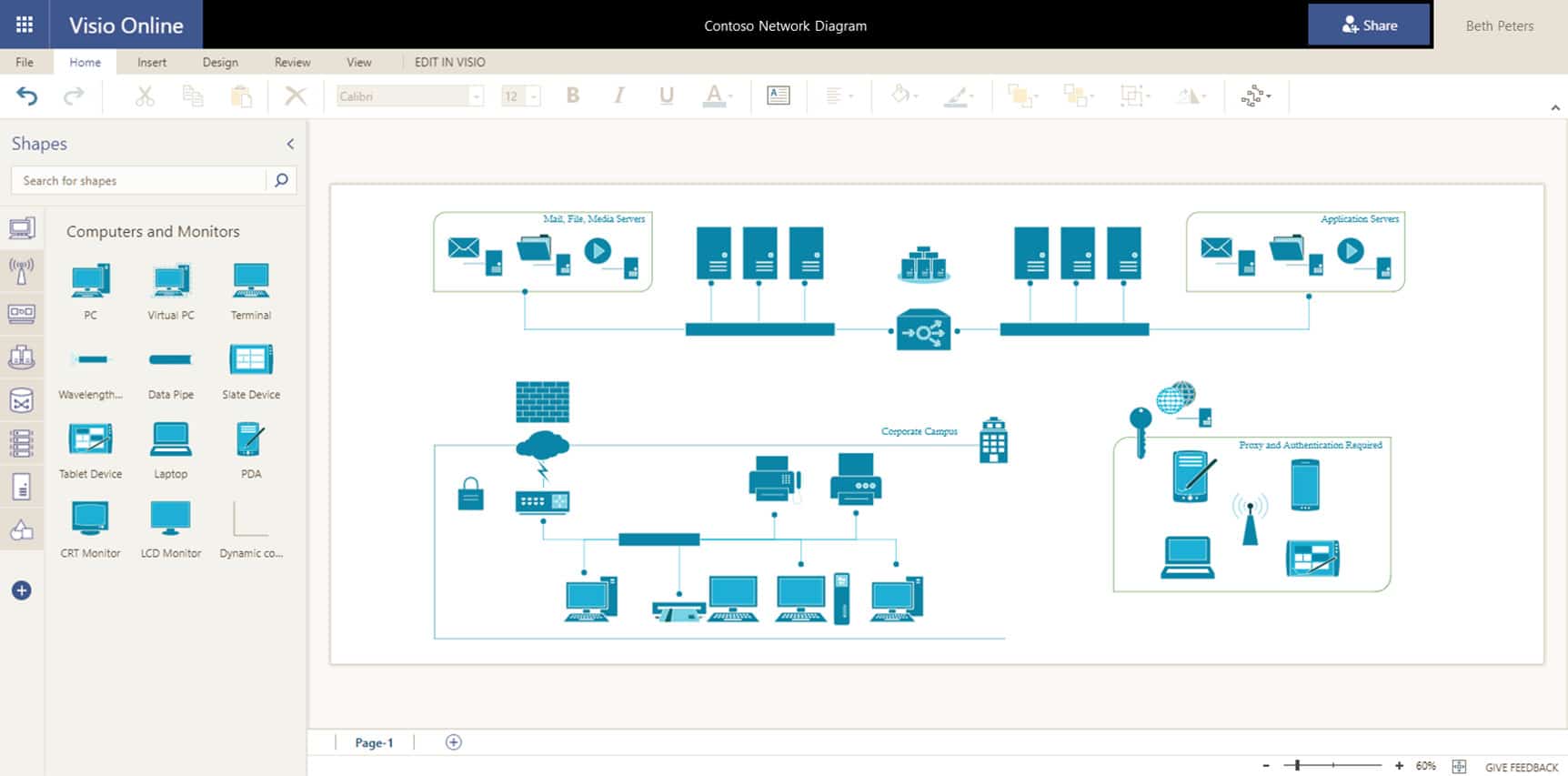
Visio
Visio is the Microsoft diagramming and vector application for creating maps and charts (including network maps). Visio isn’t technically a network mapping tool, but network administrators can use it for this purpose. However, the network diagram needs to be created manually using the “Detailed Network Diagram” template. Generally, automatic network mapping tools may be more suitable for troubleshooting and security purposes. Visio can be an inexpensive option for an enterprise unwilling to invest in automated and comprehensive network mapping software.
Getting Started With Network Mapping
As you can tell, there’s a lot of network topology mapping software out there, from simple network topology mappers and flow-chart programs to comprehensive network performance tools. When compared to some of the best free mapping software, paid products might seem expensive at first glance. However, paid network mapping and performance monitoring tools are much more comprehensive, reliable, and complete when it comes to usefully mapping your network.
I highly recommend SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor or Network Topology Mapper for professional network administrators looking for tools to help them manage their environments.
Recommended Reading:
Ultimate Guide to Network Monitoring: If you’re looking at mapping your network and using software to do so, make sure you look at this comprehensive guide on network monitoring. Understanding your network and how it functions is essential for the mapping process to be useful.
Mapping your network is vitally important for keeping on top of how it’s performing, as well as for pinpointing bottlenecks or network issues, and troubleshooting problems. But approaching this process manually with a large or complex network can quickly become overwhelming.
I’ve found using a network mapping tool is a much better approach—especially if it can map your network for you automatically. There are a number of quality tools on the market, paid and free, which I’ll go into after a review of the network mapping process. For top-line solutions I recommend SolarWinds® Network Performance Monitor and Network Topology Mapper, both easy-to-use tools capable of mapping your network along with providing important data and performance metrics.
What Are Network Maps?
There are two main levels of maps to consider: physical and logical. While open-source network mapping tools can create a physical network map, they may not offer automated scanning to ensure the map is always up to date.
There are three levels of maps to consider—physical, logical, and functional.
A physical network map diagrams all the actual components of your network, including cords, plugs, racks, ports, servers, cables, and more. A physical network map gives you a visual representation of all the material elements of your network and the connections between them.
Best Network Mapper Free
A logical map is more abstract than the physical network map. It shows the type of network topology (bus, ring, etc.), and how the data flows between the physical objects in your network. This includes IP addresses, firewalls, routers, subnets and subnet masks, traffic flow, voice gateways, and other segments of the network.
To note: Since logical and physical network maps depict the same network environment from two different perspectives, it’s best to use both types to get a more comprehensive look at your network.
A functional network map shows you how application traffic flows through the network physically. These types of network maps are only as useful as they are accurate, which means you need an appropriate and high-quality tool.
How Does Network Mapping Work?
Network mapping is the process of visualizing all the devices on your network, how they’re connected, and how the overall network is structured. The network map generally equips you with information about whether the network is functioning properly or whether any particular device has a problem.

Networks are set up in different structures, also called topologies. The structure can have a major effect on how your network functions, what happens when a device or server goes down, and how complex it is to manage. When you map your network, you’re basically mapping its topology into a visual network diagram.
Here are the main network topologies to be aware of:
- Bus – A bus network is set up in a straight line, allowing data to flow through the network from the server to each node one by one
- Ring – In a ring, network the nodes are arranged in a circle, and data can flow around the circle in one or both directions
- Tree – In a tree topology, a server has multiple branches of nodes coming off it. This is a bit more robust than a bus or ring topology, as with a tree topology, if one of the branches has a problem with a node, the rest of the network will still function. With ring and bus topologies, a problem with one node can cause the whole network to go down
- Star – A star topology has one central node with all others coming off it in a star pattern
- Mesh – A mesh network has connections between all the nodes and servers, like a lattice or mesh. It has high failover protection because if one node goes down, the network can reroute the data to get it where it needs to go
- Hybrid – A hybrid topology is simply a combination of any or all the above network structures and is very common as networks get larger
Best Network Mappers
Of course, all these types of network maps are only as useful as they are accurate, which means you need an appropriate and high-quality tool. While mapping can be done manually using tools like ping and tracert, followed by a visual mapping or vector program, this process can be prohibitively time-consuming. Similarly, if you’re considering a free network mapping solution, you should check which kind of network map it offers and whether it will give you the full visibility you need to optimize network performance.
Below, I look at some of the best network mappers on the market and what makes them stand out from the pack.
- Network Performance Monitor – Free Trial
My top pick is SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor (NPM). NPM is extremely useful for both mapping networks and determining how your network is performing. It includes a feature called NetPath, which maps your network and then provides you with information on network performance, traffic, and configuration along the entire service delivery path. You can also see performance metrics with hop-by-hop data between your central servers and your satellite offices.
NPM also features a number of network visualization graphs and charts. Insights from NPM network mapping features can easily be viewed alongside your other performance tools to provide troubleshooting assistance of your entire network. Try out a free trial of NPM for 30 days.
- Network Topology Mapper – Free Trial
SolarWinds Network Topology Mapper (NTM) is focused on network mapping. Unlike NPM, the tool doesn’t include network performance measurement capabilities. However, NTM shines in its ability to automatically plot your network to build multiple different kinds of network maps from a single scan.
The automatic scanning function is useful if you have an already established network needing to be properly mapped. It automatically detects any changes in your network topology and updates the maps accordingly. You can choose whether you want it to determine your network using SNMP, ICMP, WMI, CDP, or another method of discovery. You can also try NTM free for up to 14 days.
Paessler PRTG Network Monitor is a well-known software with monitoring and performance tools as well as reporting features and dashboards. It lets you create maps to show you devices and connections, as well as live status information for your network, so you can detect problems in one glance and troubleshoot effectively using maps as a primary source of information. You can customize your map using HTML, and you can share the map with whoever you want (company-only or external). While the maps are extremely useful, you must create them manually using the drag-and-drop map editor, which can be time-consuming.
Best Network Mapper Software
Device42 is a configuration management database with auto-discovery and application mapping tools. You can set up a schedule and Device42 will automatically scan your network and infrastructure and detect any changes as they’re made, so your network information is always up to date. It can track IP and non-IP based devices and assets, hardware, software, and interdependencies between devices, as well as resource utilization. You can also generate dependency and impact visuals using the Device42 NetFlow collector, which allows you to view topologies at different levels. Overall this is useful software, but the auto-discovery can be difficult to implement if the network is very complex, as it tends to pick up unnecessary information.
Intermapper allows you to create custom maps quickly and effectively, automatically mapping all the IP-enabled devices in your network. You can customize your maps with colors and different background options, as well as color-coded statuses to show you how the network is performing. It provides you with real-time text or email alerts if there are any issues, helping prevent your users from being affected. Intermapper works for Mac, Linux, and Windows, and offers a 30-day trial, a free version, and an enterprise version.
Nmap is a free and open-source network mapping tool that uses IP packets to determine what hosts are on the network, what services are offered by those hosts, and identify operating systems, firewalls, and other information. It runs on Windows, Linux, and Mac OS X, and can link in with other Nmap suite tools including Zenmap, Ncat, Ndiff, and Nping. Nmap comes with a learning curve, but it’s a great option if you’re working with a small business without the budget for a professional tool.
Spiceworks is a manual network mapping tool that allows you to view an interactive network diagram of how your devices work together and relate to each other. You can add, edit, move, and resize devices on the map to show how your network is structured, as well as using filters and views to show only the most important data. The network map displays lines between each node—the thicker the line, the more bandwidth is being used. However, the mapping is manual, which means you need to redo your network map every time your network changes. The Spiceworks network mapper is free, though, so it’s a good choice for someone who has the time to map a smaller, less complex network rather than a changing enterprise system.
Best Network Mapping Solution
Best Network Marketing Companies

There are a number of good network map tools on the market, but in my view, some are better equipped to handle the task than others. Some are tools you can use to help you map the network yourself. Others look at your network and map it automatically. Automatic network mappers result in fewer mistakes and missed devices, and are designed to adapt when a new server or node is added to the network. I recommend trying Network Performance Monitor as an all-in-one network map and performance tool for any size environment.
Recommended Reading
Best Network Monitoring Software – If you need to do more than map your network, look into a complete network monitoring solution. I’ve written reviews of what I consider to be the best network monitoring software.
Best Network Mapper Free
6 Best FREE Patch Management Software – Network maintenance involves more than monitoring the topology—you need to make sure you’re keeping on top of all your patches and updates, among other priorities. There are a number of free patch management solutions that can help you. Here are my top picks.